What is a Computer?
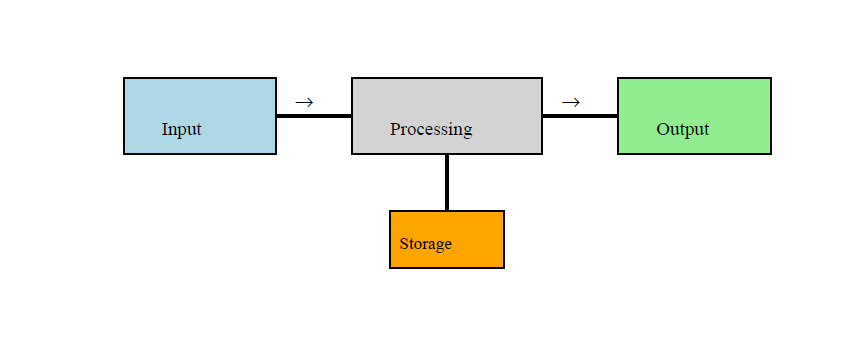
A computer is an electronic machine that takes data (input) from the user, processes it using its brain (CPU), and gives results (output). It can also store the data for future use. A computer works very fast and can do millions of calculations per second without getting tired or bored.
In Simple Words:
A computer is a smart machine that helps us do work quickly, correctly, and easily.
Real-Life Examples:
- Typing on a keyboard = input.
- Using a calculator in a math test = computer is processing data.
- Saving your assignment on a USB = storing data.
- Watching YouTube = using output (video and audio).
Main Features of a Computer:
1. Speed
- A computer can perform millions of instructions in one second (called MIPS – Million Instructions Per Second).
- Much faster than a human.
Example: A teacher takes 30 minutes to calculate marks of 50 students, but a computer can do it in seconds.
2. Accuracy
- A computer gives correct results if the input is correct.
- It does not make mistakes like humans, unless there is an error in data (called “Garbage In, Garbage Out”).
Example: If you enter wrong numbers in MS Excel, the result will also be wrong.
3. Storage
- Computers can store huge amounts of data for a long time.
- Data can be stored in hard drives, CDs, USBs, memory cards, etc.
- You can search and access stored data any time.
Example: A movie stored on your laptop can be watched again and again.
4. Automation
- Once you give instructions (program), a computer can work automatically without help.
- No need to repeat the command again and again.
Example: A printer prints 100 pages without any user help after giving the print command once.
5. Multitasking
- A computer can do many jobs at the same time without confusion.
- You can listen to songs, download files, and type notes at the same time.
Example: Using MS Word while listening to music and browsing the internet.
Basic Parts of a Computer
A computer system is made of two main components:
1. Hardware – The physical parts of the computer you can touch.
2. Software – The programs and applications that give instructions to the hardware.
Input and Output Devices
A. Input Devices
These devices are used to enter data into the computer.
| Device | Function |
|---|---|
| Keyboard | For typing letters, numbers, commands |
| Mouse | For pointing, clicking, and selecting |
| Scanner | To convert printed pictures or text into digital form |
| Microphone | To enter sound or voice |
| Webcam | To input live video or images |
B. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
CPU is called the “brain of the computer”. It processes all instructions and manages data.
It has 3 main parts:
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) – Performs math and logic operations.
- CU (Control Unit) – Controls all parts of the computer.
- Registers – Small storage inside the CPU for quick data access.
Example: When you solve 5 + 3, the CPU adds the numbers and gives the result.
C. Output Devices
These devices show the result of the processed data.
| Device | Function |
|---|---|
| Monitor | Displays text, images, videos (like a TV screen) |
| Printer | Prints documents and pictures on paper |
| Speakers | Give output as sound or music |
| Projector | Shows computer screen on a large wall or screen |
D. Storage Devices
These are used to save data permanently or temporarily.
| Device | Type | Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Drive (HDD/SSD) | Permanent | Up to 4 TB or more |
| USB Flash Drive | Portable | 4 GB – 256 GB |
| CD/DVD | Portable | 700 MB – 4.7 GB |
| Memory Card | Portable | 2 GB – 128 GB |
Types of Computers
| Type | Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Computer (PC) | For general use at home, school, offices | Desktop computer |
| Laptop | Portable computer | HP, Dell, Lenovo laptops |
| Tablet/Smartphone | Small, touchscreen devices for daily use | Android, iPhone, iPad |
| Mainframe Computer | Used by big companies to process large data | Used by banks, airlines |
| Supercomputer | Most powerful and fast, used for scientific purposes | Used in weather forecasting, space research |
Uses of Computers in Daily Life
| Field | Use |
|---|---|
| Education | Online learning, research, computer labs, digital libraries |
| Business | Making reports, managing sales, communication, record-keeping |
| Healthcare | Storing patient data, checking medical reports, digital x-rays |
| Banking | Online banking, ATM services, customer records |
| Entertainment | Watching movies, playing games, using social media |
| Communication | Emails, video calling, chatting, Zoom meetings |
| Science & Technology | Simulations, weather predictions, research |
Why is it important to learn computers?
Because almost every field today needs basic computer knowledge. From writing assignments to applying for jobs, using the internet, or doing research—computers are everywhere.
Conclusion
Computers are now an essential part of life. Whether it’s school, home, office, or hospital—computers help in saving time, increasing accuracy, and doing work faster.